SEELIFE is a PNRR project aiming at strengthening the Italian network of Eurobioimaging (EUBI), an European research infrastructure that has 4 nodes in Italy, one being ALM (Advanced Light Microscopy), with 5 sites, one in Genoa shared between IIT and the Physics Department of the University. The Genoa unit takes part in WP1 (Technological empowering of the biological imaging services) and is Leader of WP4 (Empowering training activity and dissemination).
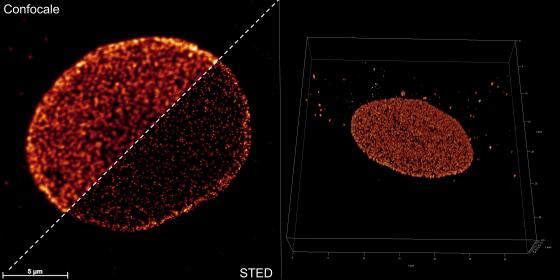
The commercial Minflux instrument by Abberior has been implemented in a center already equipped with fluorescence confocal systems Leica TCS SP5 and Leica Stellaris8 TAU STED with white light and multiphoton lasers, this latter setup being part of the DIFILAB.
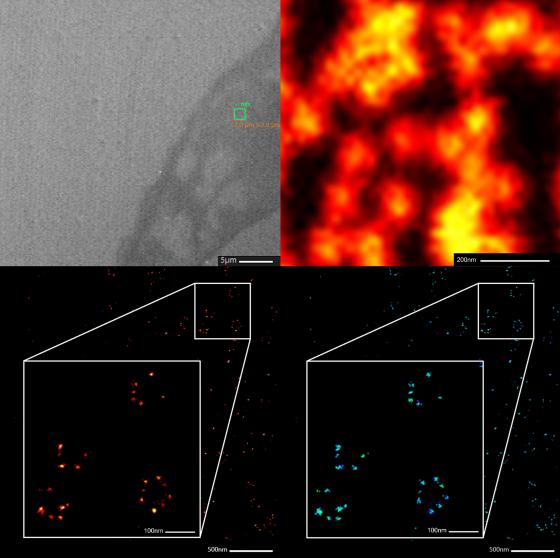
Minflux setup specifications:
- Inverted optical microscope Olympus IX83 with oil immersion objective 100X 1.4 NA
- Sample 3D stabilizing piezoelectric stage with feedback loop control based on identification of gold nanobeads as reference fiducial markers
- 640 nm wavelength Minflux laser, 405 nm wavelength confocal laser
Minflux performance:
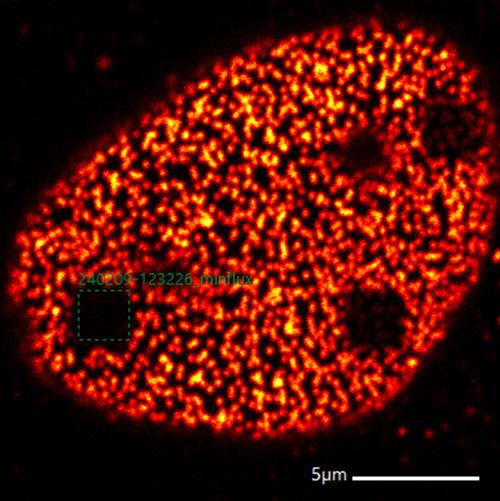
- 2D/3D imaging of biological samples (living and fixed) with resolution better than 5 nm
- Tracking of single molecules in living cells with sampling frequency up to 10 kHz (i.e. one in 100 µs) with resolution better than 20 nm
Minflux, based of blinking of fluorophores in proper enviroment, allows one to reach a resolution down to the molecular scale of around 2 nm. In this technique the diffraction limit is overcome by distinguishing the fluorescent labels in time in addition to the sample space, thanks to the principle of localization already adopted for STORM/PALM. Localization here is done in a more clever way thanks to scanning and identification algorhytms that make resolution about one order of magnitude smaller than previously accessible. On the other hand, at this level of performance, defining a specific biological problem to be tackled becomes of critical importance, as well as the corresponding sample preparation appropriate for the respective goals. Until today, the Minflux results have been somewhat limited in most cases to visualization of model systems (nuclear pores or "rulers" based on chemical spacers used to test actual resolution) or to tracking of molecules with already largely known behavior such as kinesin.
In order to have the largest number of possible experiments being devised as well as to provide a useful service, in agreement with the project goals, the Genoa center is made accessible to all the European researchers that may be interested in accessing its instruments, on request, with different options (joint scientific research or facility service, in the latter case with possible fees requested for instrument maintainance, depending on the type of user). We are currently discussing with Abberior to organize a training service for new users of other European microscopy centers.